The French against the crisis of democracy: Immigration, Populism, Trump, Europe...
Main takeaways
Methotodology
Study results
The French and the United States
The rise of populism
Between the fear of globalization, rejection of immigration, rise of Islamism and populism, in a context of upheaval in the world’s order, relations between Europe and the United States are suffering through the most important crisis in their history.
The weakening of the transatlantic relationship, multilateralism, NATO, as well as the divisions within the European Union are all the more threatening as they manifest themselves into a context of the rise of competing models, the first of which are Russia and China.
In 2016, in a context already marked by Islamist attacks, the refugee crisis and the populist upsurge, AJC Europe and the Foundation for Political Innovation organized a day of reflection to draw attention to the erosion of the democratic world. Today, we reiterate the event, two years after the election of Donald Trump, while the refugee crisis continues to have an impact throughout Europe, favoring notably new populist breakthroughs.
To support the second edition of the Sursaut, we asked the polling institute Ifop to carry out an opinion survey in order to understand the public’s view of Franco-American relations and of the future of democracies (the survey was conducted in France with a sample of 1,007 people, interviewed from the 10th to the 11th of September 2018).
Main takeaways
The Franco-German friendship is perceived as stronger than ever, and Putin’s Russia worries twice the number of French people than Trump’s America does.
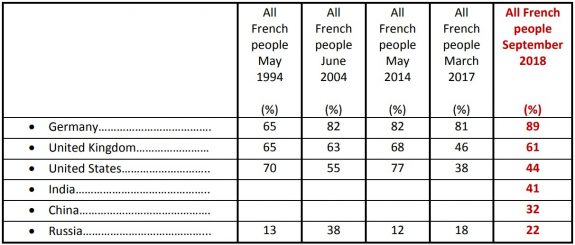
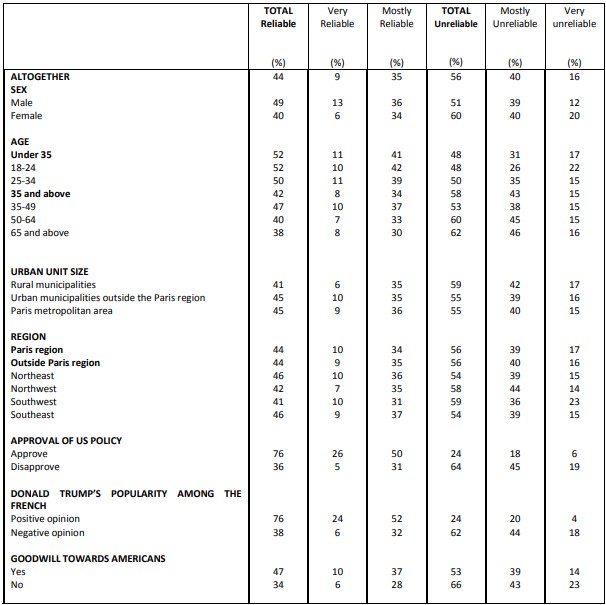
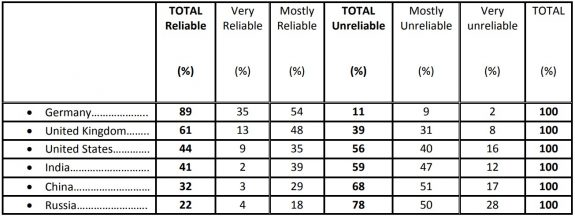
More than ever, Germany is viewed by the French as “an ally or a safe partner country” (89%) compared to 61% for the United Kingdom and 44% for the United States. The French’s judgement of Germany has not been this favorable since 1994.
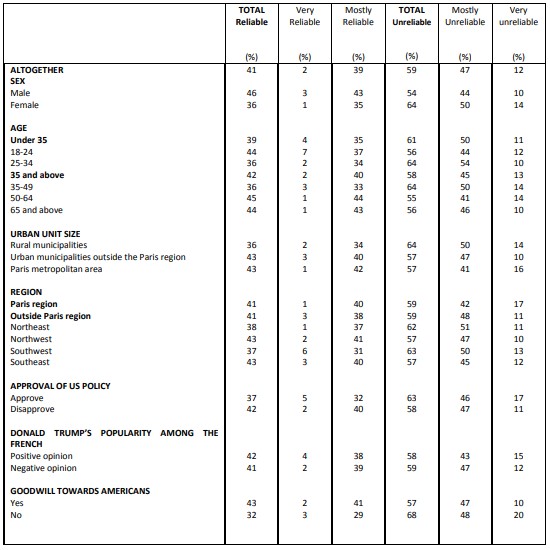
It should be noted that despite a lower level of confidence, the image of the United Kingdom, more than a year after Brexit, has improved significantly (61%) compared to 2017 (46%).
A positive judgment of the US has nonetheless risen by six percentage points since March of 2017 (38%).
Finally, in the case of non-European powers, the French have most confidence in India (41%), ahead of China (32%) and finally Russia (22%), which comes last.
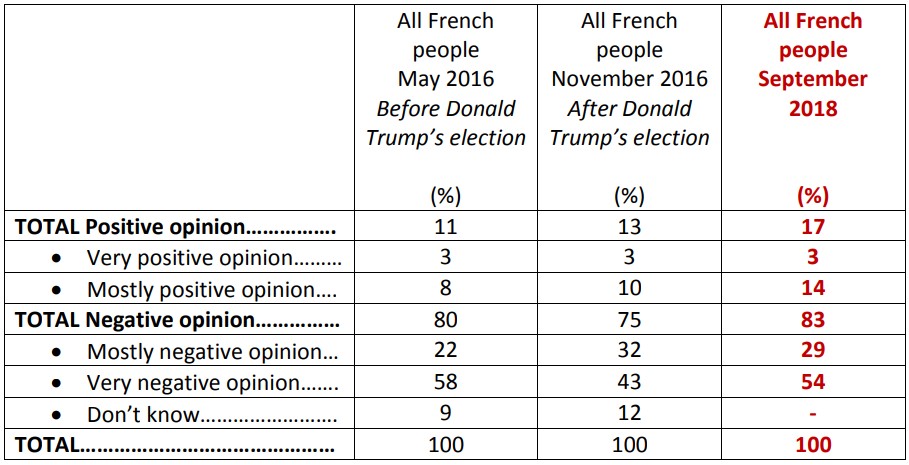
The French do not confuse Trump with Americans.
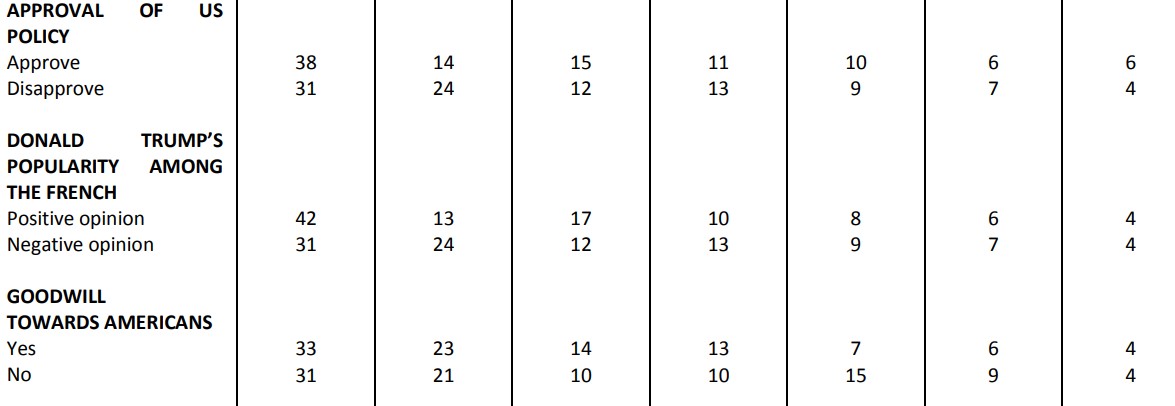
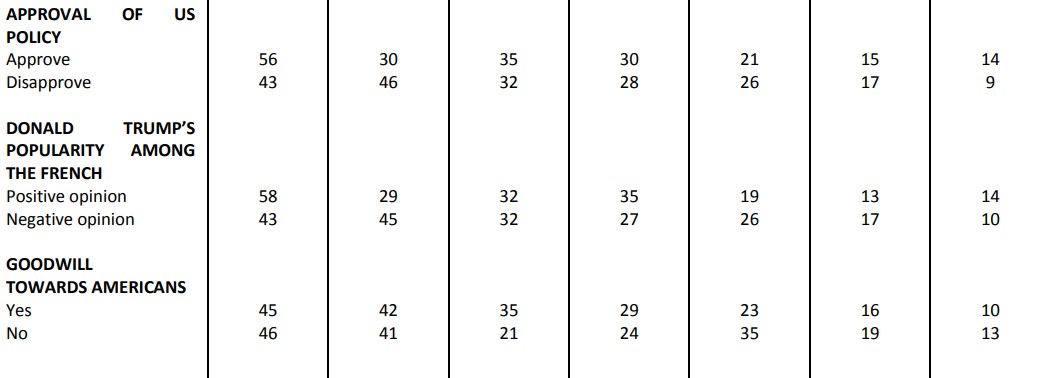
While a significant proportion of French people still consider the United States as a partner (44%), judgments made on the policies of the American President elicit wide disapproval (80%). Similarly, our survey reveals that 83% of French people have a poor opinion of Donald Trump as president, a number which has increased by eight points since the day after his election (75%).
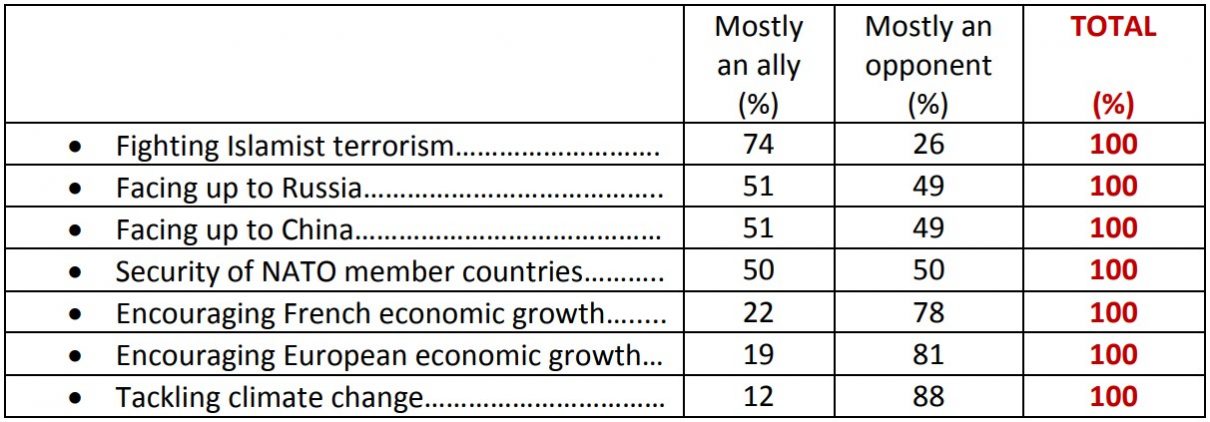
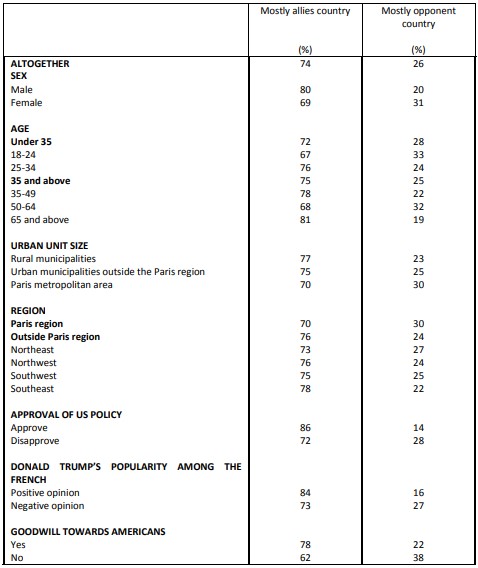
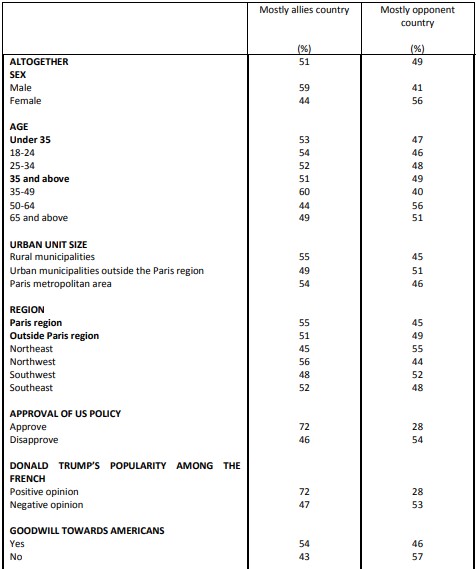
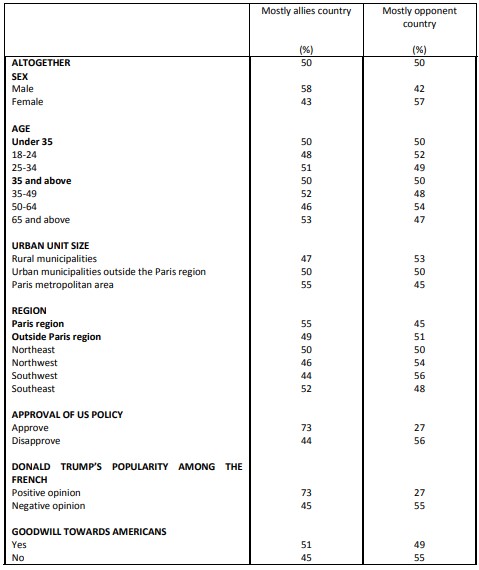
The United States is firstly considered an ally in the fight against Islamist terrorism (74%). To go up against Russia, barely more than one in two French people (51%) qualify the United States as an ally, and 49% consider the country an “opponent”! In general, to ensure the security of NATO member countries, 50% of French people look to the United States as an ally, and 50% as an opponent.
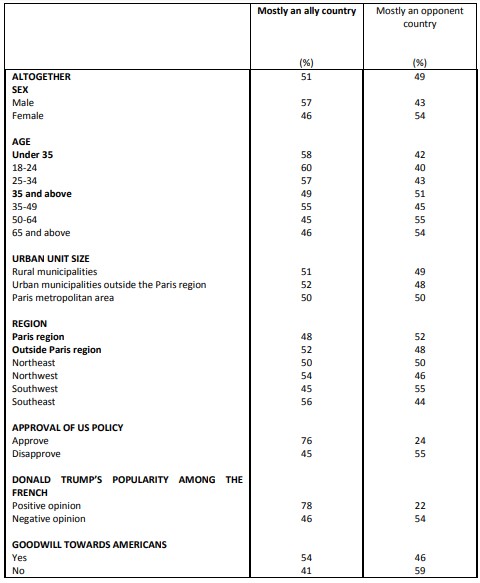
In terms of economic growth, the French are massively (78%) watching the United States as an “adversary”, both in regards to France (78%) as well as to the European Union as a whole (81%). It is about the fight against global warming that the French are the most numerous to consider the United States as an adversary.
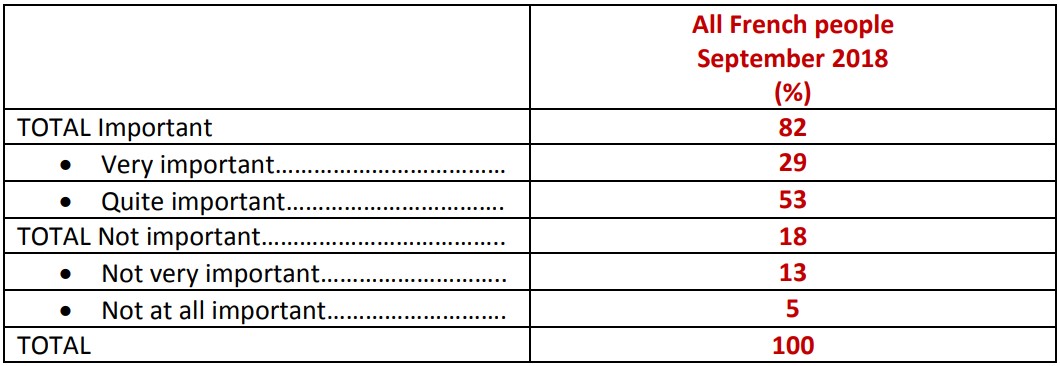
While the French severely judge the President of the United States, they do not confuse him with the American people. In fact, 75% of those surveyed consider that Donald Trump is a president who does not represent the image of Americans. This confirms the friendship that a very broad majority of French respondents (79%) say they feel for Americans. Similarly, the French remain above all convinced of the need to preserve the relationship between Europe and the United States: they are 82% to judge the preservation of this relationship as important in the years to come.
Fragile democracy: migration crisis and populist upsurge.
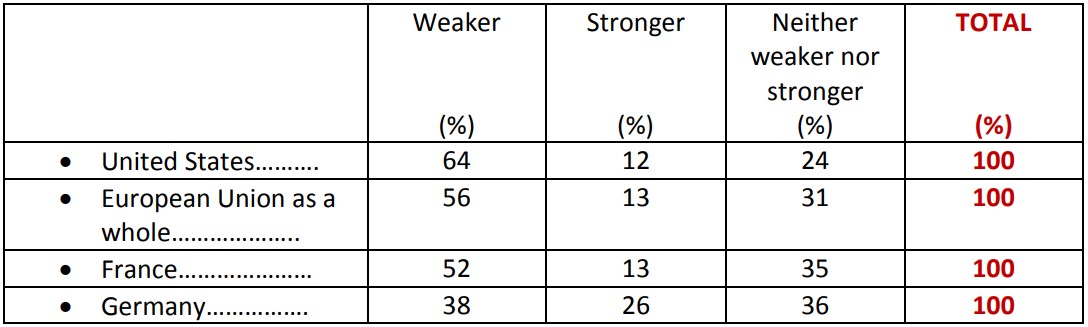
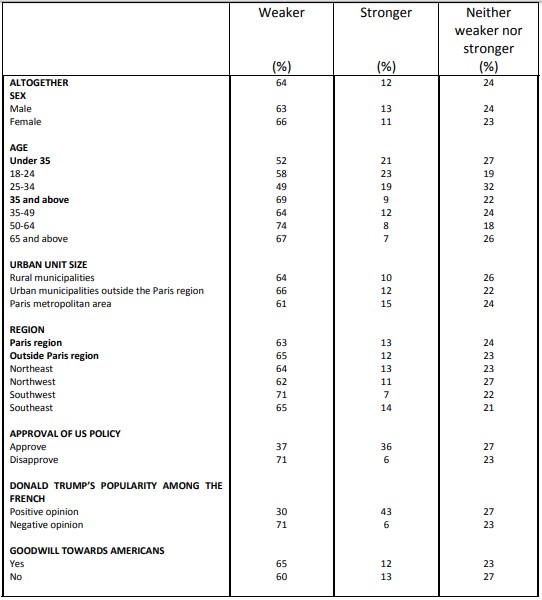
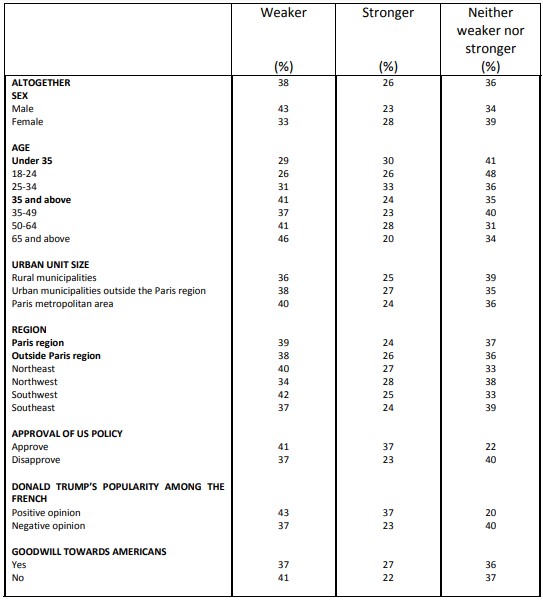
According to the survey, by comparing the current situation to that of a few years ago, democracy appears more fragile in the United States (64%) than in the EU as a whole (56%), and even less so in France (52%). A large minority (38%) also consider the German democracy as more fragile.
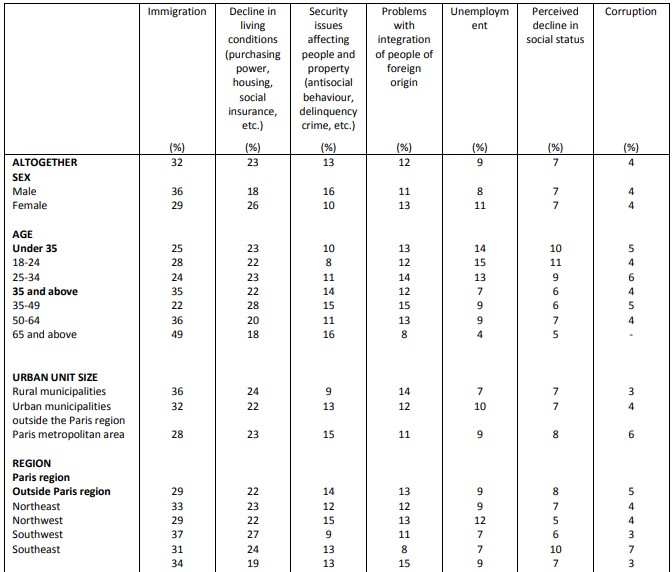
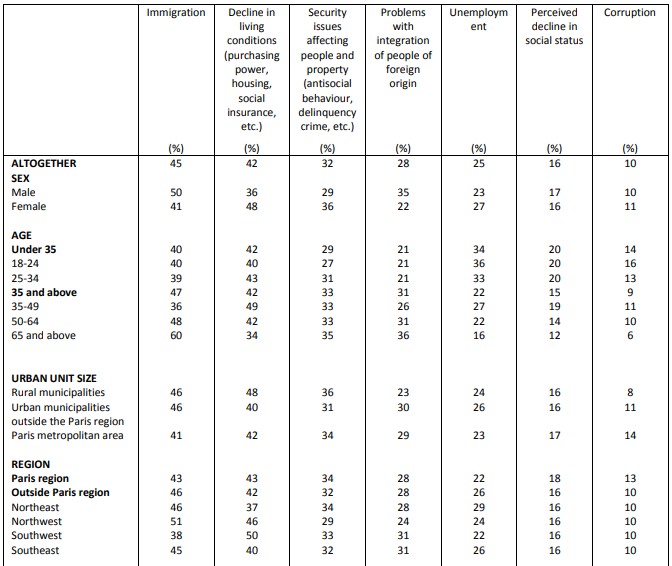
According to respondents, 32% of French people cite that the rise of populism and protest votes in Europe can be explained by immigration, followed by the 23% that cited degradations of living conditions – purchasing power, housing, social insurance, etc., the 12% that cited problems regarding the security of individuals and property – incivility, delinquency, criminality, 13% that cited the integration of those with foreign origins, unemployment (9%), the feeling of social decommissioning (7%) and corruption (4%).
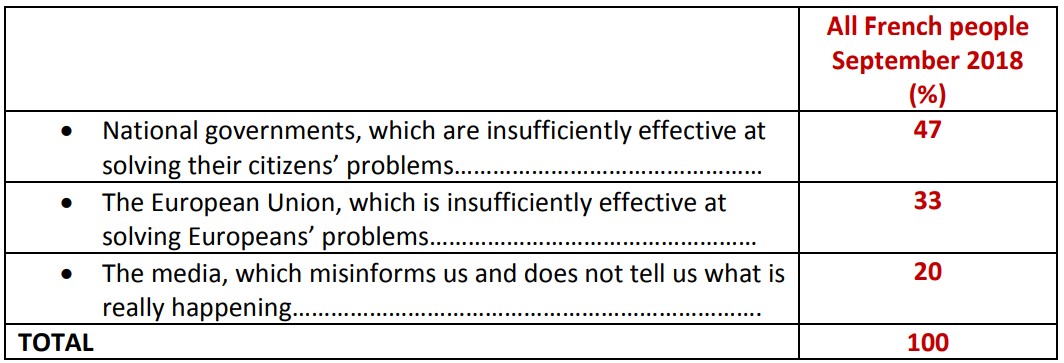
The French believe that those most responsible for the rise in populism in Europe are first and foremost national governments (47%), far ahead of the European Union (33%). The idea that the media could be responsible for poorly informing us is shared by only 20% of respondents.
Methotodology
This document presents the results of a study conducted by Ifop. It is fully compliant with scientific ethical principles of polling. Its findings reflect the state of public opinion at the time that it was conducted and should not be regarded as a prediction.
Ifop’s express consent is required for any full or partial publication.
Study conducted by Ifop on behalf of Le Sursaut and the Fondation pour l’innovation politique
Note regarding margins of error
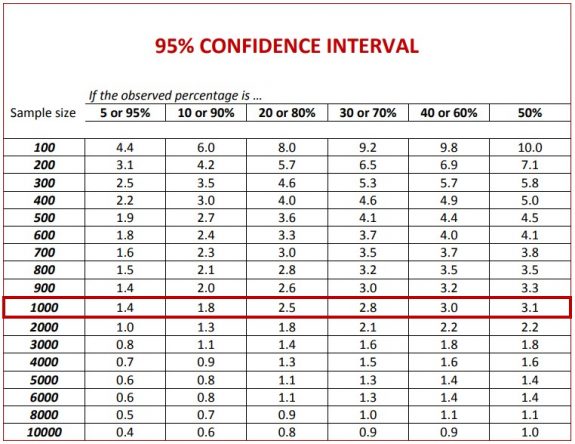
Using statistical theory, it is possible to measure the uncertainty of each result in a survey. This uncertainty is expressed as a confidence interval either side of the observed value in which the real value has a determined probability of occurring. This uncertainty, commonly referred to as the ‘margin of error’ varies depending on sample size and the observed percentage, as shown in the table.
Example reading of the table: in a sample of 1,000 people, if the measured percentage is 10%, the margin of error is 1.8. The real percentage is therefore between 8.2% and 11.8%.
Study results
The French and the United States
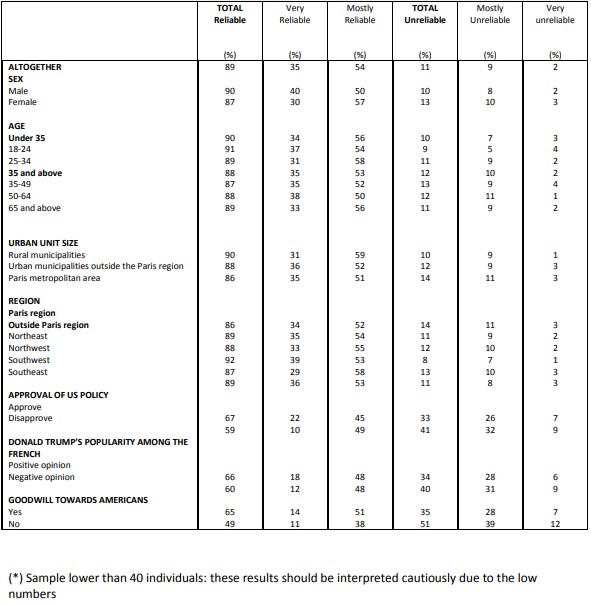
Perceived reliability of various allies or partners
Question: Please indicate whether you consider each of the following countries to be a very reliable, mostly reliable, mostly unreliable or very unreliable ally or partner for France.
– Summary Table – “TOTAL reliable” –
Perceived reliability of various allies or partners
Question: Please indicate whether you consider each of the following countries to be a very reliable, mostly reliable, mostly unreliable or very unreliable ally or partner for France.
Perceived reliability of various allies or partners Germany
Perceived reliability of various allies or partners United Kingdom
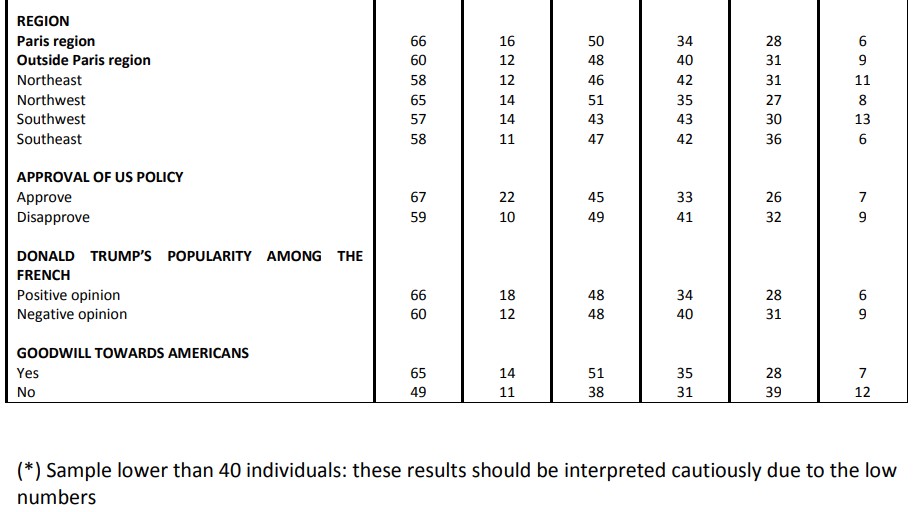
Perceived reliability of various allies or partners United States
Perceived reliability of various allies or partners India
Perceived reliability of various allies or partners China
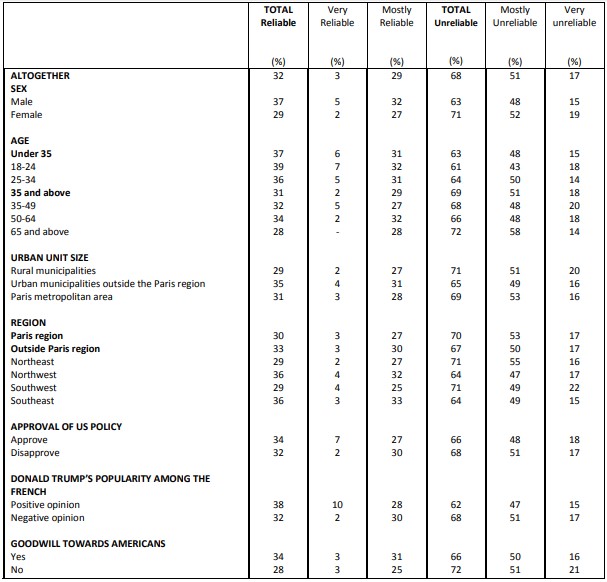
Perceived reliability of various allies or partners Russia
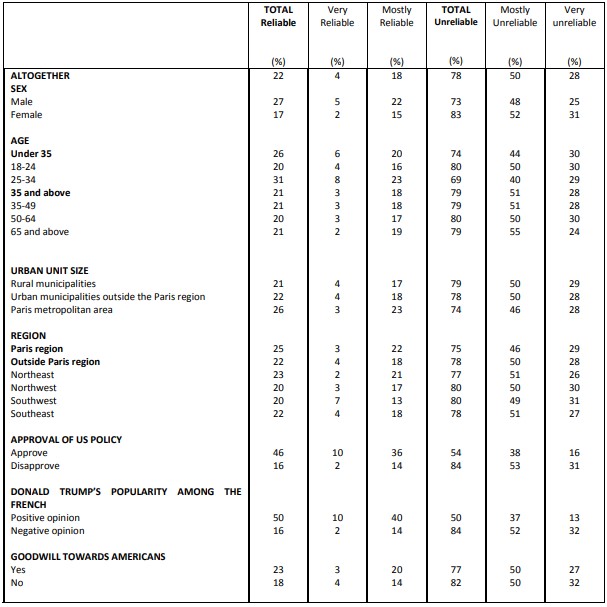
Approval of US policy
Question: In general, do you approve or disapprove of US policy?
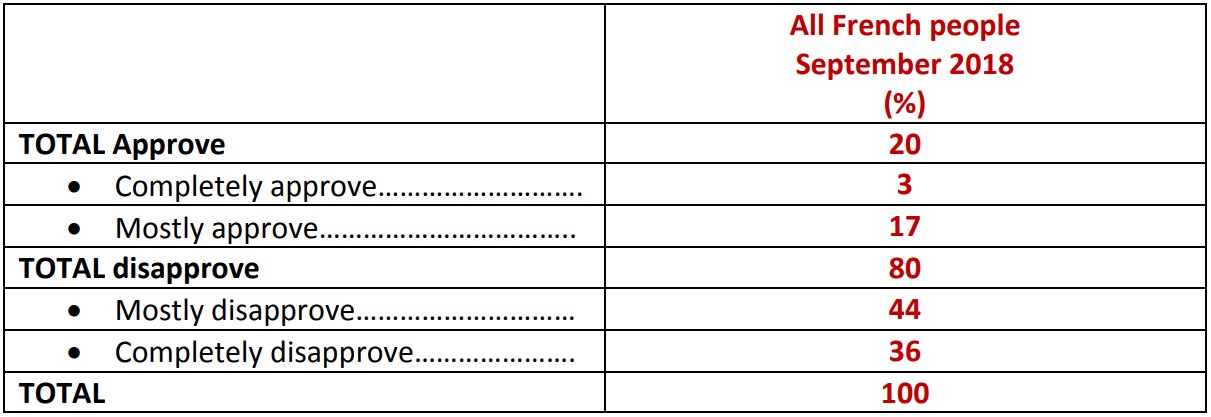
Approval of US policy
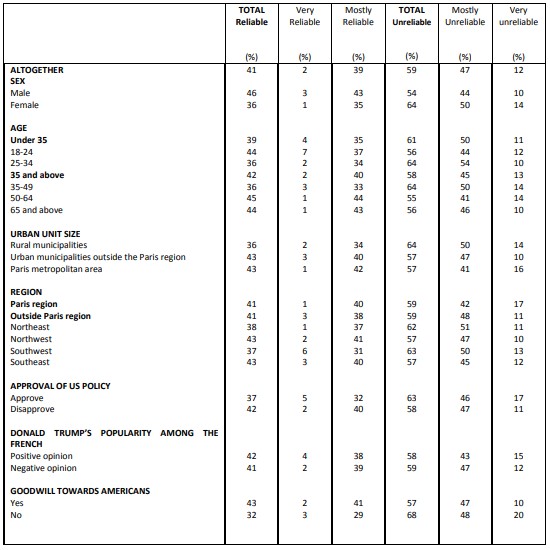
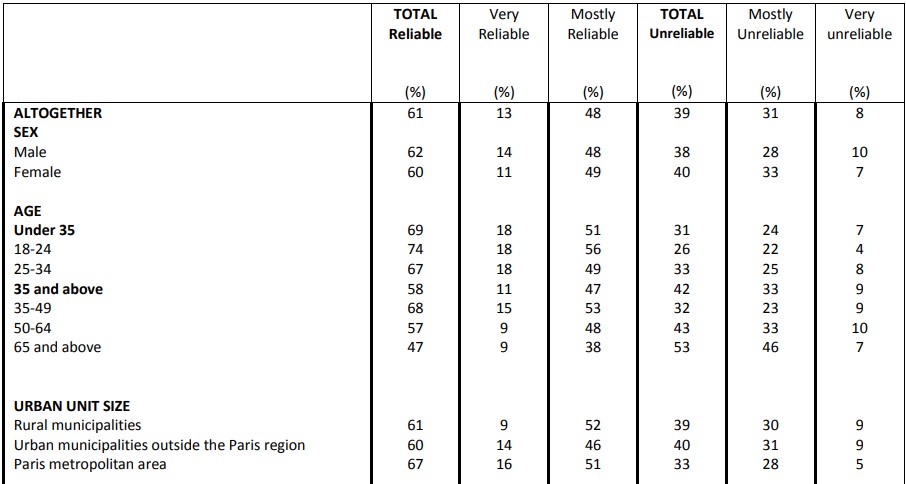
Perceptions of Franco-American cooperation on various issues
Question: With regard to the following issues, would you say that the United States is mostly an ally or opponent of France?
Perceptions of Franco-American cooperation on various issues Fighting Islamist terrorism
Perceptions of Franco-American cooperation on various issues Facing up to Russia
Perceptions of Franco-American cooperation on various issues Facing up to China
Perceptions of Franco-American cooperation on various issues The security of NATO member states
Perceptions of Franco-American cooperation on various issues Encouraging French economic growth
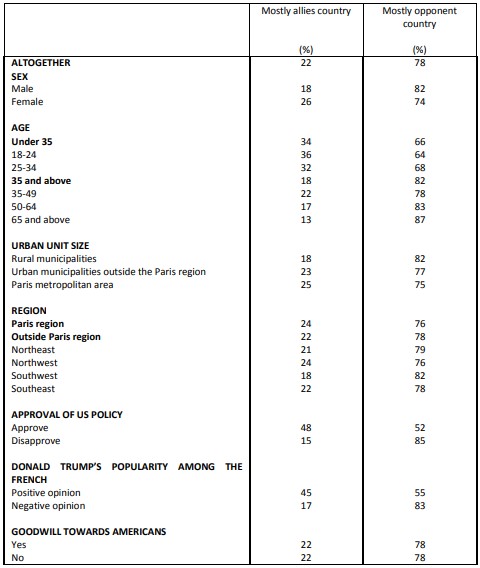
Perceptions of Franco-American cooperation on various issues Encouraging European economic growth
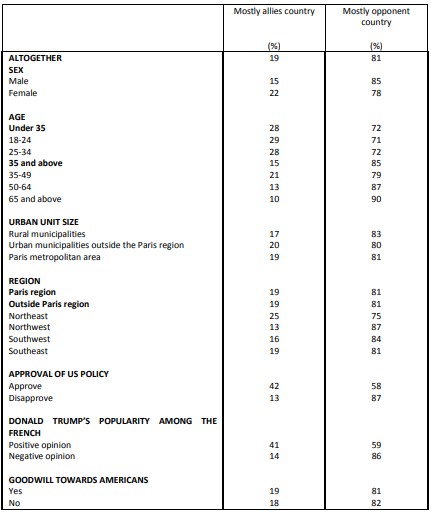
Perceptions of Franco-American cooperation on various issues
Tackling climate change
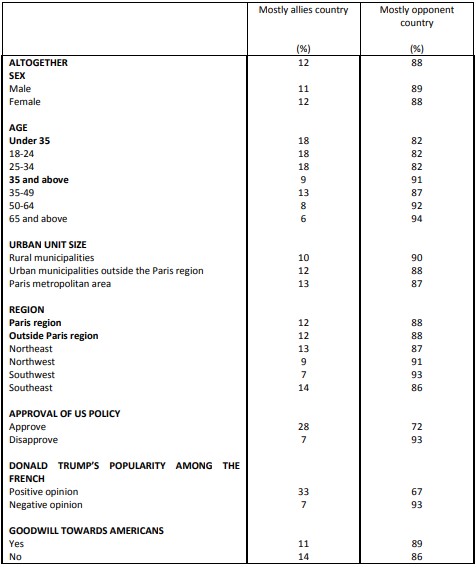
Donald Trump’s approval rating among the French
Question: Would you say that you personally have a positive or negative opinion of Donald Trump as US president?
Donald Trump’s approval rating among the French
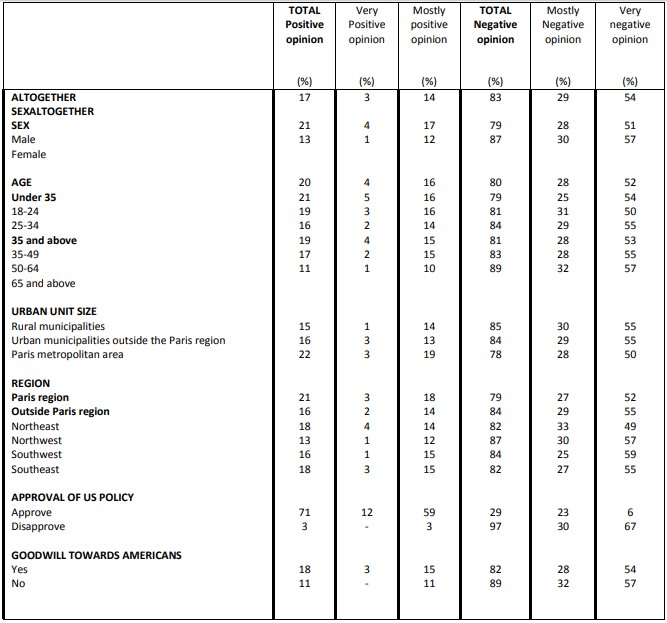
Perceived degree of similarity between Donald Trump and Americans in general
Question: In your opinion, is Donald Trump a president who is …?

Perceived degree of similarity between Donald Trump and Americans in general
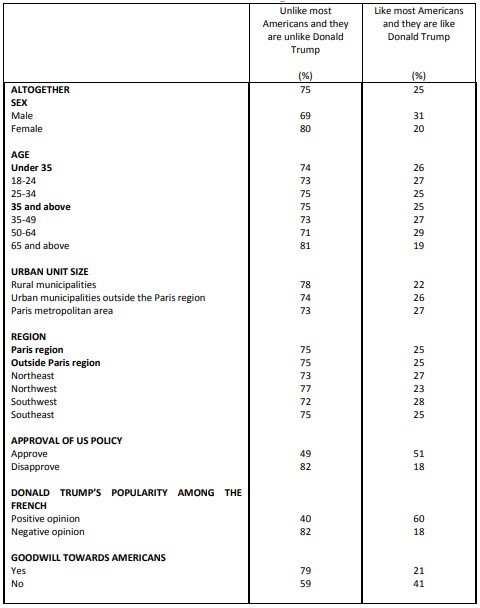
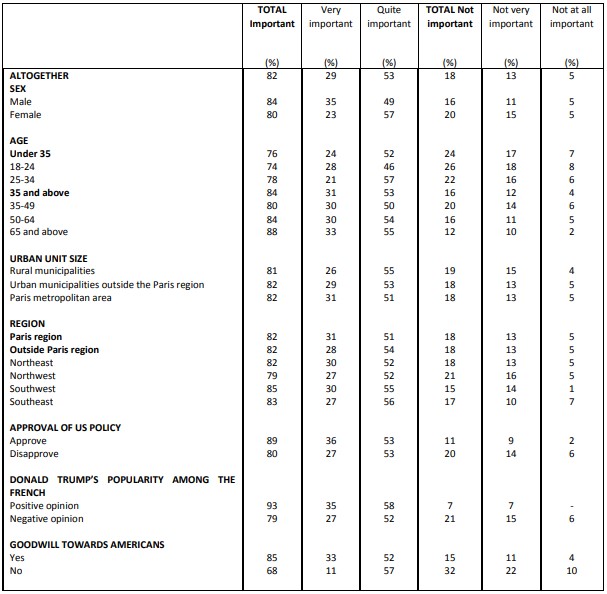
Perceived importance of maintaining relations between Europe and the United States
Question: Some people believe that relations between Europe and Donald Trump’s United States are currently in serious crisis. Do you think it is important or not important to maintain these relations in future years?
Perceived importance of maintaining relations between Europe and the United States
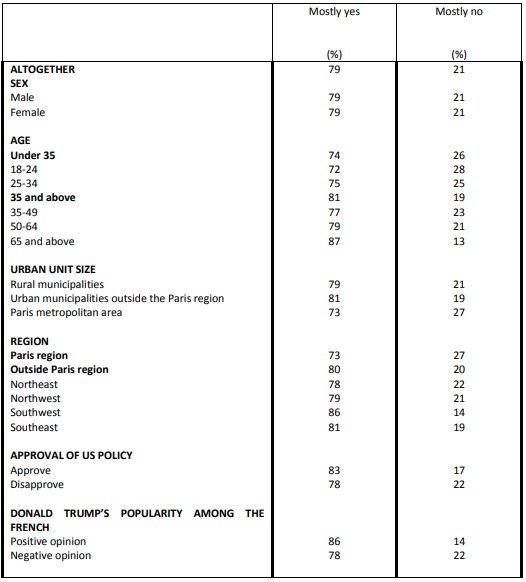
Goodwill towards Americans
Question: Regardless of Donald Trump, would you say that you feel benevolent towards Americans?
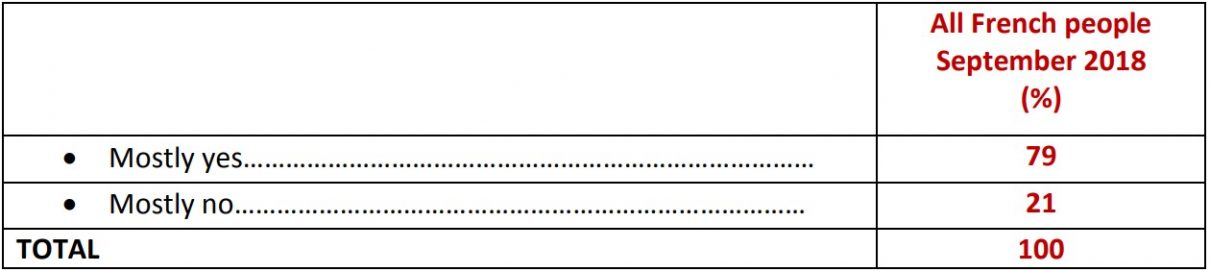
Goodwill towards Americans
The rise of populism
Perceived strength of democracy in various countries
Question: Compared to the situation several years ago, would you say that democracy is weaker, stronger, or neither weaker nor stronger in each of the following countries or territorial units?
Perceived strength of democracy in various countries United States
Perceived strength of democracy in various countries European Union as a whole
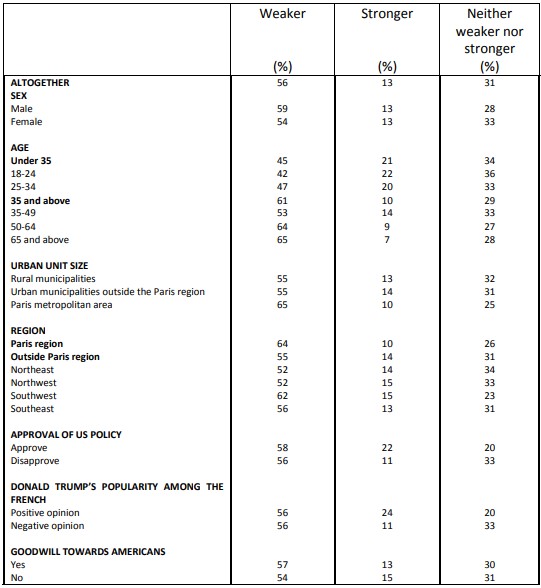
Perceived strength of democracy in various countries France
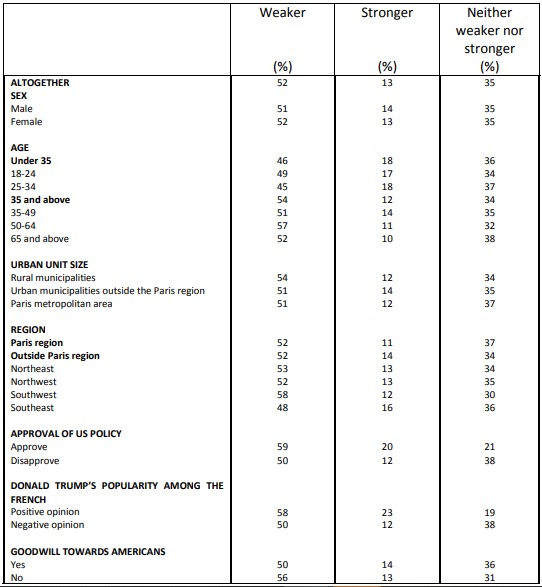
Perceived strength of democracy in various countries Germany
Causes of the rise of populism in Europe
Question: In your opinion, which of the following issues is the most likely explanation for the rise of populism and protest voting in Europe? Please rank your answers first and second.
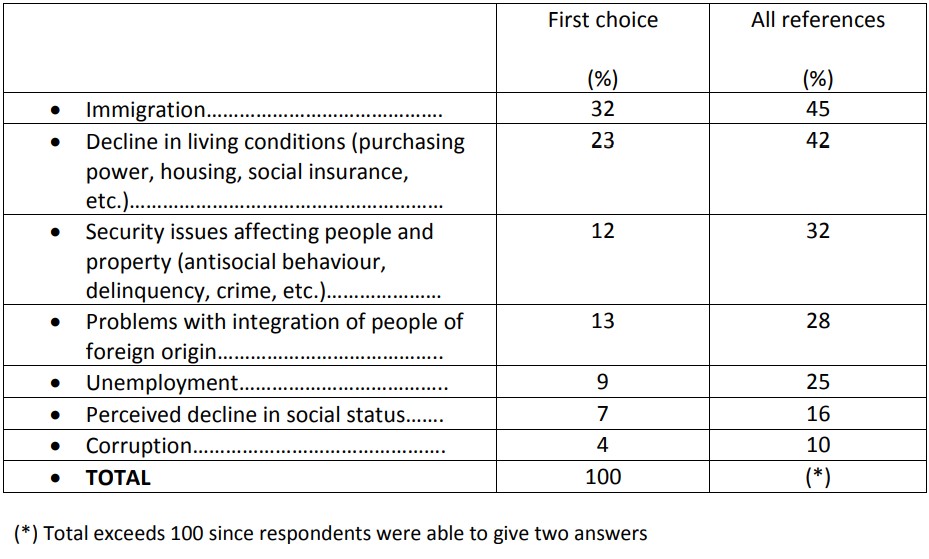
Causes of the rise of populism in Europe First choice
Causes of the rise of populism in Europe
All references
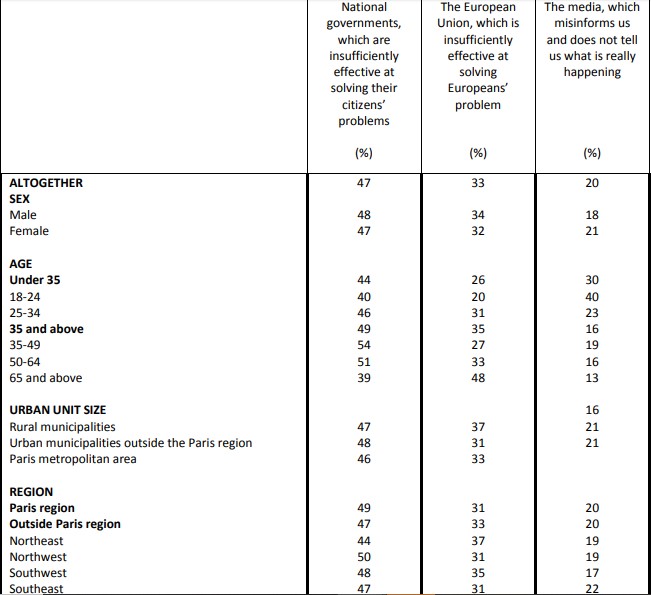
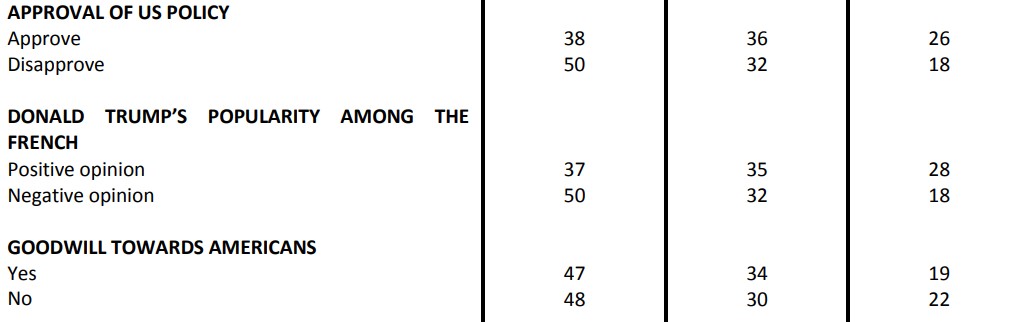
The authority most responsible for the rise in populism in Europe
Question: Which of the various powers below would you say is most responsible for the rise of populism and protest voting in Europe?
The authority most responsible for the rise in populism in Europe














No comments.